I used to think that running an organization was equivalent to
conducting a symphony orchestra. But I don't think that's quite it;
it's more like jazz. There is more improvisation.
— Warren Bennis
Good leaders are
made not born. If you have the desire and
willpower, you can become an effective leader. Good leaders develop
through a never ending process of self-study, education, training, and
experience (Jago, 1982). This guide will help you through that process.
To inspire your workers into higher levels of teamwork, there are certain things you must
be, know, and,
do.
These do not come naturally, but are acquired through continual work
and study. Good leaders are continually working and studying to improve
their leadership skills; they are NOT resting on their laurels.
Definition of Leadership
The meaning of a message is the change which it produces in the image. — Kenneth Boulding in The Image: Knowledge in Life and Society
Before we get started, lets define leadership. Leadership is a
process by which a person influences others to accomplish an objective
and directs the organization in a way that makes it more cohesive and
coherent. This definition is similar to Northouse's (2007, p3)
definition — Leadership is a process whereby an individual influences a
group of individuals to achieve a common goal.
Leaders carry out this process by applying their leadership
knowledge and
skills. This is called
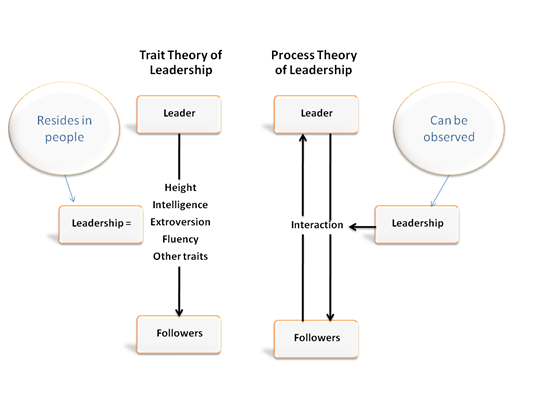
Process Leadership (Jago, 1982). However, we know that we have traits that can influence our actions. This is called
Trait Leadership
(Jago, 1982), in that it was once common to believe that leaders were
born rather than made. These two leadership types are shown in the chart
below (Northouse, 2007, p5):
While leadership is learned, the skills and knowledge processed by
the leader can be influenced by his or hers attributes or traits, such
as
beliefs,
values,
ethics, and
character. Knowledge and skills contribute directly to the
process of leadership, while the other attributes give the leader certain characteristics that make him or her unique.
Skills, knowledge, and attributes make the
Leader, which is one of the:
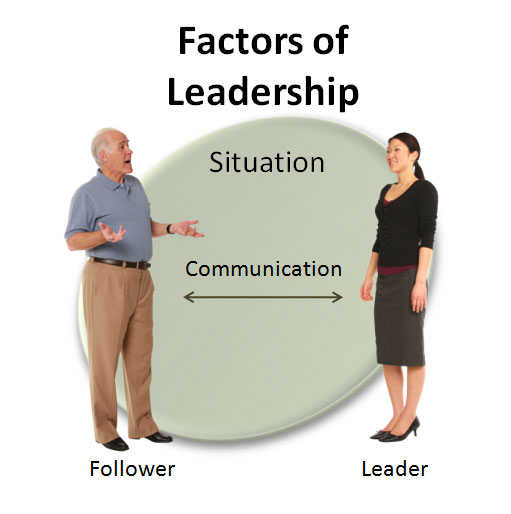
Four Factors of Leadership
There are four major factors in leadership (U.S. Army, 1983):
Leader
You must have an honest understanding of who you are, what you know,
and what you can do. Also, note that it is the followers, not the leader
or someone else who determines if the leader is successful. If they do
not trust or lack confidence in their leader, then they will be
uninspired. To be successful you have to convince your followers, not
yourself or your superiors, that you are worthy of being followed.
Followers
Different people require different styles of leadership. For example,
a new hire requires more supervision than an experienced employee. A
person who lacks motivation requires a different approach than one with a
high degree of motivation. You must know your people! The fundamental
starting point is having a good understanding of human nature, such as
needs, emotions, and motivation. You must come to know your employees'
be, know, and
do attributes.
Communication
You lead through two-way
communication.
Much of it is nonverbal. For instance, when you “set the example,” that
communicates to your people that you would not ask them to perform
anything that you would not be willing to do. What and how you
communicate either builds or harms the relationship between you and your
employees.
Situation
All situations are different. What you do in one situation will not
always work in another. You must use your judgment to decide the best
course of action and the leadership style needed for each situation. For
example, you may need to confront an employee for inappropriate
behavior, but if the confrontation is too late or too early, too harsh
or too weak, then the results may prove ineffective.
Also note that the
situation normally has a greater effect
on a leader's action than his or her traits. This is because while
traits may have an impressive stability over a period of time, they
have little consistency across situations (Mischel, 1968). This is why a
number of leadership scholars think the
Process Theory of Leadership is a more accurate than the
Trait Theory of Leadership.
Various forces will affect these four factors. Examples of forces
are your relationship with your seniors, the skill of your followers,
the informal leaders within your organization, and how your organization
is organized.
Boss or Leader?
Although your position as a manager, supervisor, lead, etc. gives you
the authority to accomplish certain tasks and objectives in the
organization (called
Assigned Leadership), this
power does not make you a leader, it simply makes you the
boss (Rowe, 2007). Leadership differs in that it makes the followers
want to achieve high goals (called
Emergent Leadership), rather than simply bossing people around (Rowe, 2007). Thus you get
Assigned Leadership by your position and you display
Emergent Leadership by influencing people to do great things.
Bass' Theory of Leadership
Bass' theory of leadership states that there are three basic ways to
explain how people become leaders (Stogdill, 1989; Bass, 1990). The
first two explain the leadership development for a small number of
people. These theories are:
- Some personality traits may lead people naturally into leadership roles. This is the Trait Theory.
- A crisis or important event may cause a person to rise to the
occasion, which brings out extraordinary leadership qualities in an
ordinary person. This is the Great Events Theory.
- People can choose to become leaders. People can learn leadership
skills. This is the Transformational or Process Leadership Theory. It is
the most widely accepted theory today and the premise on which this
guide is based.
Total Leadership
What makes a person want to follow a leader? People want to be guided
by those they respect and who have a clear sense of direction. To gain
respect, they must be ethical. A sense of direction is achieved by
conveying a strong vision of the future.
When a person is deciding if she respects you as a leader, she does
not think about your attributes, rather, she observes what you
do so that she can know who you really
are.
She uses this observation to tell if you are an honorable and trusted
leader or a self-serving person who misuses authority to look good and
get promoted. Self-serving leaders are not as effective because their
employees only obey them, not follow them. They succeed in many areas
because they present a good image to their seniors at the expense of
their workers.
Be Know Do
The basis of good leadership is honorable character and selfless
service to your organization. In your employees' eyes, your leadership
is everything you do that effects the organization's objectives and
their well-being. Respected leaders concentrate on (U.S. Army, 1983):
- what they are [be] (such as beliefs and character)
- what they know (such as job, tasks, and human nature)
- what they do (such as implementing, motivating, and providing direction).
What makes a person want to follow a leader? People want to be
guided by those they respect and who have a clear sense of direction. To
gain respect, they must be ethical. A sense of direction is achieved by
conveying a strong vision of the future.
The Two Most Important Keys to Effective Leadership
According to a study by the Hay Group, a global management
consultancy, there are 75 key components of employee satisfaction (Lamb,
McKee, 2004). They found that:
- Trust and confidence in top leadership was the single most reliable predictor of employee satisfaction in an organization.
- Effective communication by leadership in three critical areas was the key to winning organizational trust and confidence:
- Helping employees understand the company's overall business strategy.
- Helping employees understand how they contribute to achieving key business objectives.
- Sharing information with employees on both how the company is
doing and how an employee's own division is doing — relative to
strategic business objectives.
So in a nutshell — you must be
trustworthy and you have to be able to
communicate a vision of where the organization needs to go. The next section,
Principles of Leadership, ties in closely with this key concept.
Principles of Leadership
To help you
be, know, and
do, follow these eleven principles of leadership (U.S. Army, 1983). The later chapters in this
Leadership guide expand on these principles and provide tools for implementing them:
- Know yourself and seek self-improvement - In order to know yourself, you have to understand your be, know, and do,
attributes. Seeking self-improvement means continually strengthening
your attributes. This can be accomplished through self-study, formal
classes, reflection, and interacting with others.
- Be technically proficient - As a leader, you must know your job and have a solid familiarity with your employees' tasks.
- Seek responsibility and take responsibility for your actions
- Search for ways to guide your organization to new heights. And when
things go wrong, they always do sooner or later — do not blame others.
Analyze the situation, take corrective action, and move on to the next
challenge.
- Make sound and timely decisions - Use good problem solving, decision making, and planning tools.
- Set the example - Be a good role model for your employees. They must not only hear what they are expected to do, but also see. We must become the change we want to see - Mahatma Gandhi
- Know your people and look out for their well-being - Know human nature and the importance of sincerely caring for your workers.
- Keep your workers informed - Know how to communicate with not only them, but also seniors and other key people.
- Develop a sense of responsibility in your workers - Help to develop good character traits that will help them carry out their professional responsibilities.
- Ensure that tasks are understood, supervised, and accomplished - Communication is the key to this responsibility.
- Train as a team
- Although many so called leaders call their organization, department,
section, etc. a team; they are not really teams...they are just a group
of people doing their jobs.
- Use the full capabilities of your organization - By
developing a team spirit, you will be able to employ your organization,
department, section, etc. to its fullest capabilities.
Attributes of Leadership
If you are a leader who can be trusted, then those around you will grow to respect you. To be such a leader, there is a
Leadership Framework to guide you:
BE KNOW DO
BE a professional. Examples: Be loyal to the organization, perform selfless service, take personal responsibility.
BE a professional who possess good
character traits. Examples: Honesty, competence, candor, commitment, integrity, courage, straightforwardness, imagination.
KNOW the four factors of leadership — follower, leader, communication, situation.
KNOW yourself. Examples: strengths and weakness of your character, knowledge, and skills.
KNOW human nature. Examples: Human needs, emotions, and how people respond to stress.
KNOW your job. Examples: be proficient and be able to train others in their tasks.
KNOW your organization. Examples: where to go for help, its climate and culture, who the unofficial leaders are.
DO provide
direction. Examples: goal setting, problem solving, decision making, planning.
DO implement. Examples:
communicating, coordinating, supervising, evaluating.
DO motivate. Examples: develop morale and
esprit de corps in the organization, train, coach, counsel.
Environment
Every organization has a particular work environment, which dictates
to a considerable degree how its leaders respond to problems and
opportunities. This is brought about by its heritage of past leaders and
its present leaders.
Goals, Values, and Concepts
Leaders exert influence on the
environment via three types of actions:
- The goals and performance standards they establish.
- The values they establish for the organization.
- The business and people concepts they establish.
Successful organizations have leaders who set high standards and
goals
across the entire spectrum, such as strategies, market leadership,
plans, meetings and presentations, productivity, quality, and
reliability.
Values reflect the concern the organization has for its employees,
customers, investors, vendors, and surrounding community. These values
define the manner in how business will be conducted.
Concepts define what products or services the organization will offer and the methods and processes for conducting business.
These goals, values, and concepts make up the organization's
personality
or how the organization is observed by both outsiders and insiders.
This personality defines the roles, relationships, rewards, and rites
that take place.
Roles and Relationships
Roles are the positions that are defined by a set of expectations
about behavior of any job incumbent. Each role has a set of tasks and
responsibilities that may or may not be spelled out. Roles have a
powerful effect on behavior for several reasons, to include money being
paid for the performance of the role, there is prestige attached to a
role, and a sense of accomplishment or challenge.
Relationships are determined by a role's tasks. While some tasks are
performed alone, most are carried out in relationship with others. The
tasks will determine who the role-holder is required to interact with,
how often, and towards what end. Also, normally the greater the
interaction, the greater the liking. This in turn leads to more frequent
interaction. In human behavior, its hard to like someone whom we have
no contact with, and we tend to seek out those we like. People tend to
do what they are rewarded for, and friendship is a powerful reward. Many
tasks and behaviors that are associated with a role are brought about
by these relationships. That is, new task and behaviors are expected of
the present role-holder because a strong relationship was developed in
the past, either by that role-holder or a prior role-holder.
Culture and Climate
There are two distinct forces that dictate how to act within an organization:
culture and climate.
Each organization has its own distinctive culture. It is a
combination of the founders, past leadership, current leadership,
crises, events, history, and size (Newstrom, Davis, 1993). This results
in
rites: the routines, rituals, and the “way we do things.”
These rites impact individual behavior on what it takes to be in good
standing (the norm) and directs the appropriate behavior for each
circumstance.
The climate is the feel of the organization, the individual and
shared perceptions and attitudes of the organization's members
(Ivancevich, Konopaske, Matteson, 2007). While the culture is the deeply
rooted nature of the organization that is a result of long-held formal
and informal systems, rules, traditions, and customs; climate is a
short-term phenomenon created by the current leadership. Climate
represents the beliefs about the “feel of the organization” by its
members. This individual perception of the “feel of the organization”
comes from what the people believe about the activities that occur in
the organization. These activities influence both individual and team
motivation and satisfaction, such as:
- How well does the leader clarify the priorities and goals of the organization? What is expected of us?
- What is the system of recognition, rewards, and punishments in the organization?
- How competent are the leaders?
- Are leaders free to make decisions?
- What will happen if I make a mistake?
Organizational climate is directly related to the leadership and
management style of the leader, based on the values, attributes, skills,
and actions, as well as the priorities of the leader. Compare this to
“ethical climate” — the feel of the organization about the activities
that have ethical content or those aspects of the work environment that
constitute ethical behavior. The ethical climate is the feel about
whether we do things right; or the feel of whether we behave the way we
ought to behave. The behavior (character) of the leader is the most
important factor that impacts the climate.
On the other hand, culture is a long-term, complex phenomenon.
Culture represents the shared expectations and self-image of the
organization. The mature values that create tradition or the “way we do
things here.” Things are done differently in every organization. The
collective vision and common folklore that define the institution are a
reflection of culture. Individual leaders, cannot easily create or
change culture because culture is a part of the organization. Culture
influences the characteristics of the climate by its effect on the
actions and thought processes of the leader. But, everything you do as a
leader will affect the climate of the organization.
For information on culture, see
Long-Term Short-Term Orientation
The Process of Great Leadership
The road to great leadership (Kouzes & Posner, 1987) that is common to successful leaders:
- Challenge the process - First, find a process that you believe needs to be improved the most.
- Inspire a shared vision - Next, share your vision in words that can be understood by your followers.
- Enable others to act - Give them the tools and methods to solve the problem.
- Model the way - When the process gets tough, get your hands dirty. A boss tells others what to do, a leader shows that it can be done.
- Encourage the heart - Share the glory with your followers' hearts, while keeping the pains within your own.
Next Steps
References
Bass, Bernard (1990).
From transactional to transformational leadership: learning to share the vision.
Organizational Dynamics, 18, (3), Winter, 1990, 19-31.
Ivancevich, J., Konopaske, R., Matteson, M. (2007).
Organizational Behavior and Management. New York: McGraw-Hill Irwin.
Jago, A. G. (1982). Leadership: Perspectives in theory and research.
Management Science, 28(3), 315-336.
Kouzes, James M. & Posner, Barry Z. (1987).
The Leadership Challenge. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Lamb, L. F., McKee, K. B. (2004).
Applied Public Relations: Cases in Stakeholder Management. Mahwah, New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Routledge.
Mischel, W. 1968.
Personality and Assessment . New York: Wiley.
Newstrom, J. & Davis, K. (1993).
Organization Behavior: Human Behavior at Work. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Northouse, G. (2007).
Leadership theory and practice. (3rd ed.) Thousand Oak, London, New Delhe, Sage Publications, Inc.
Rowe, W. G. (2007).
Cases in Leadership. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications
Stogdill, R. M.(1989).
Stogdill's Handbook of Leadership: A Survey of Theory and Research. Bass, B. (ed.) New York: Free Press.
U.S. Army. (October 1983).
Military Leadership (FM 22-100). Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office.